| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Introduction
...
opConfig 4 is the NMIS 9 compatible version. In this guide, you will learn all you need to start using opConfig.
...
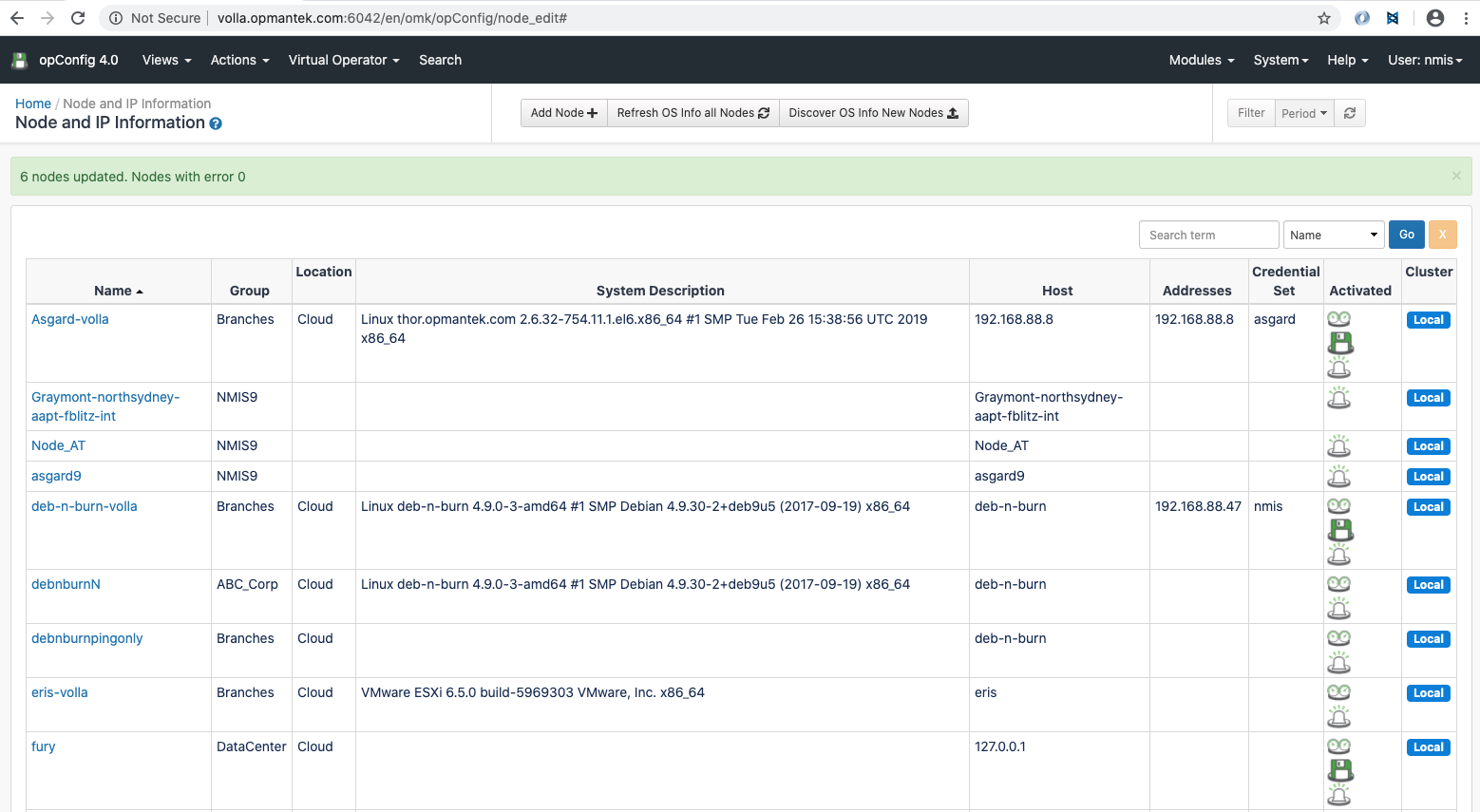
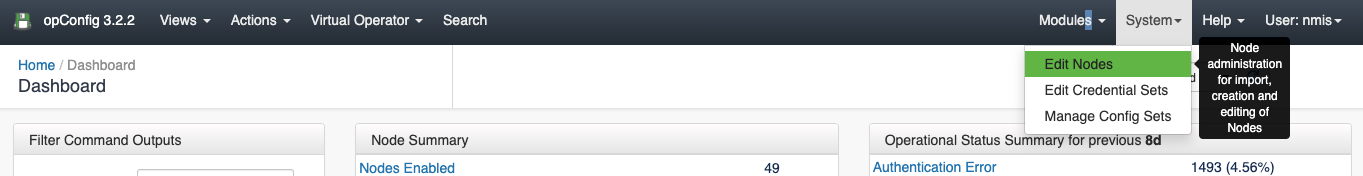
Once opConfig has been installed, we need to set up the nodes. For this, we go to System > Edit Nodes.
All the local and remote nodes (Remote nodes are seen since version 4.1.1) are listed here:
Click in the button "Refresh OS Info all Nodes" for to update the OS Info for all the local nodes. In this case, it would not take into account if the node is active for opConfig or not for a node to be selected.
This button will update the OS information for a node based on the file OS_Rules.nmis, located in the installation configuration directory by default. This These rules are based, mostly, in on the sysDescr configuration attribute. For this to be set, the community string must be correct and the device should had have been successfull successfully polled from NMIS at least , once. We can check this attribute - information, among others - , in the node information, by clicking in the node name.
...
We can also set up this configuration using the cli tool.
Note that, for remote nodes (Since version 4.1.1):
- The information will be updated in the poller also.
- If the node cannot be edited, the node won't be saved (As the changes will be overwritten by the opHA synchronisation).
- Is important that the poller has installed opConfig version 4.1.1 or higher.
- A remote node cannot be removed from the Primary.
Steps to set up a Node
If a node has been added, these are the steps to perform for this node to be ready to work with opConfig:
- Verify if the SysDescr field is filled Settings > General. What if it isn't? In this case, something is going on with the node. Here is some troubleshooting to perform:
- There is connectivity with the device?
- Is the community correct?
- Perform an update and review if the node is choosing the right model
- Discover OS Info This will fill the OS Info configuration
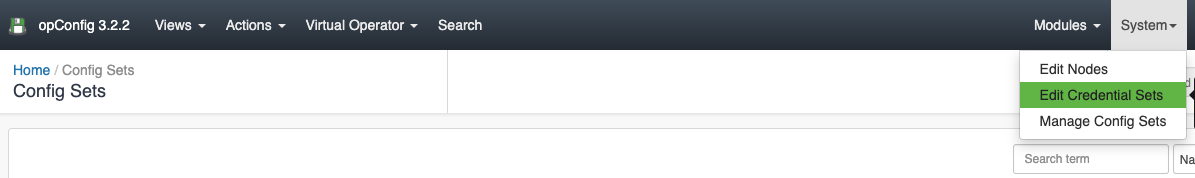
- Discover Connection Detail This will review the credentials that match. Please, make sure a Credential Set is filled in System > Edit Credential Sets
- Test Connection The last step is test the Connection with the device
If you need further debugging information for each step, you can use the cli tool with the debug option.
opConfig GUI Features
...
Views
...
No nodes match your selections and the config set filters! A config set has a set of filters that has to mach with the selected node properties. For example, the selected Config set has the following filter:
| Code Block |
|---|
"filter" : {
"activated.opConfig" : 1,
"connection_info.transport" : "SSH",
"name" : [
"node1",
"node2",
"node3"
]
}, |
...
The Virtual Operator is used to help create jobs comprised of commands sets to be run on various nodes, reporting to see job results and troubleshooting to diagnoses nodes which raise conditions. You can find a complete Virtual Operator guide in this link.
Nodes Management
From the System > Edit Nodes menu we can see all nodes, a node details and Edit or add a new node. From the node details, we can Test the connection to a Node, or Discover the Node.
From opConfig 4.0.0, nodes information is shared between NMIS and opConfig, so the "Import Nodes from NMIS" option is not available anymore.
Credential Sets
Credentials for all connections made by opConfig are configurable from the opConfig GUI ONLY. Before anything else you need to create sets of credentials to access you devices. At this point in time, opConfig supports only Telnet and SSH, and for SSH password-based authentication and RSA with no passphrase is supported.
...
It is also important to review and set accordingly the purging policies.
The opConfig Daemon
...
The opConfig daemon, opconfigd process, will run in a loop performing the following operations:
- Process queued jobs: Which are created using the cli tool for a cron job or manually, from the GUI in "Virtual Operator Job" or "Schedule Configuration Changes", or by the daemon. The daemon will process 3 types of jobs:
- config
- command
- discover
- Watch over nmis {config_logs} directory for "Node Configuration Change" events and create a new job for active nodes marked as "Auto Command Collection". Will add the tags specified in the configuration item opconfigd_run_tags_on_update. This feature can be turned off in nmis 9 setting the configuration item log_node_configuration_events.
Only "command" type jobs will be saved in the queue, to better keep track of the operations run.
Related Configuration for Change Notification
See the documentation for What constitutes a change, and when should opConfig create new revisions
Useful Configuration Items
This configuration items will affect some running daemon aspects (Please, make sure you have restarted daemon once a configuration item - <omk_dir>/conf/opCommon.nmis - is changed):
- opconfigd_max_processes: The number of child process
- opconfigd_update_rate: How many cycles the process will run before restarted. Default, is 10.
- opconfigd_update_delay: Schedule the "Node Configuration Change" jobs in opconfigd_update_delay seconds.
Related readings
...
- opConfig 4 Getting Started Guide
- opConfig 4 release notes
- opConfig 4 Troubleshooting
- opConfig CLI tool