This guide covers basic configuration for adding new nodes, providing access credentials and checking operation.
There is an advanced configuration guide which then covers compliance management, creating support for new operating systems.
Credentials for all connections made by opConfig are configurable from the opConfig GUI ONLY. Before anything else you need to create sets of credentials to access you devices. At this point in time, opConfig supports only Telnet and SSH, and for SSH only password-based authentication is supported.
Select the menu "System", then "Edit Credential Sets". Credential sets can be shared by any number of nodes.
Each credential set has to have a unique name, by which it is referenced in the nodes' connection settings. The description field is self-explanatory and optional.
A credential set has to specify a User Name property, which is used when logging in to the nodes the set applies to. At this time, opConfig supports only password-based authentication at the node, and the Password property of the credential set establishes the primary password for this user name.
SSH Key-based authentication is supported from version 3.0.2. Considerations:
As a key example configuration:
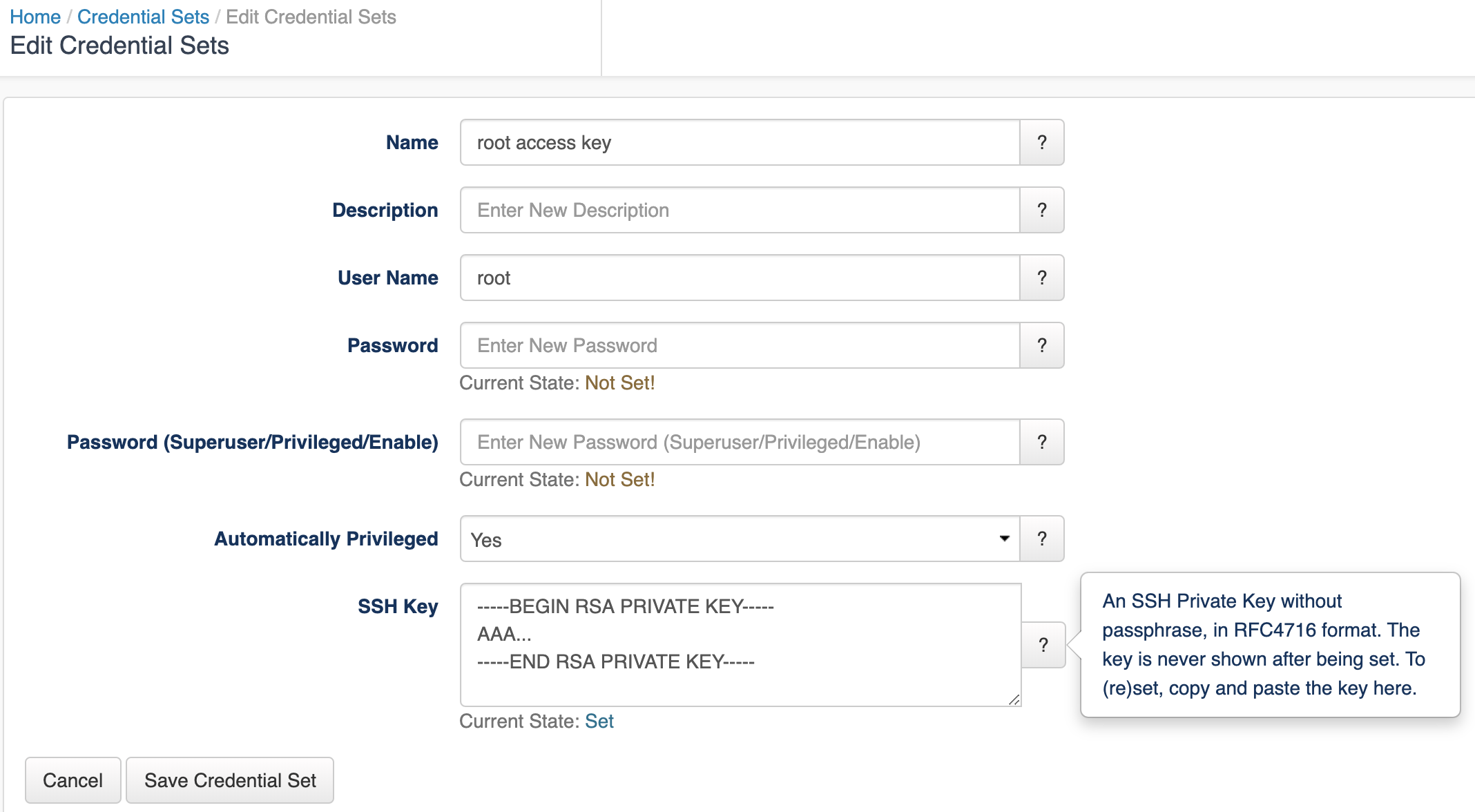
Some commands cannot be performed by an unprivileged user, which is why opConfig also supports elevating the privileges on demand. To control this, a credential set can optionally include a Superuser/Privileged/Enable Password. Depending on the node's platform and personality, different mechanisms will be used to gain increased privileges:
enable command.bash (the default for Unix-like systems), the command sudo is used to become the superuser. Sudo therefore needs to be installed and configured on such nodes, and the User Name in question needs to be authorized for sudo.Naturally not all commands require elevated privileges; see the section on Command Sets for how to determine and configure those.
Please note that the Credential Set editing dialogs never show existing passwords (or their length or existence); You can only overwrite password entries. All credential sets are stored in the database in encrypted form.
To tell opConfig to run commands for a node it needs to be told about the node's existence and what properties the node has (e.g. what platform, what OS, what credential set, what protocol to use to contact the node ). Adding a node for opConfig can be done using the GUI or the command line tools opconfig-cli.pl and . You can add node information manually to opConfig, or you can import node's info from NMIS or OpenAudit.opnode_admin.pl
opConfig can connect to any node (and run commands for it) as long as it has valid connection settings for it (and as long as it is not disabled for opConfig).
Import is only available for opConfig version prior to 4.0.0. opConfig versions >= 4.0.0 share that information in the database. |
If you successfully import the node from NMIS you should only need to add the credential set and the transport protocol (which are in the connection tab). Import generally works for "Linux" like devices and for Cisco devices. For all other device types you simply need to add some details by hand. You will see what configuration you MUST still add displayed as part of the "Edit Node" screen.
 The problem reports are fairly self-explanatory (and clickable).
The problem reports are fairly self-explanatory (and clickable).
command_sets.nmis" file) that opConfig uses, makes association between the OS and maybe a version and maybe a major release or train and the command to issue and how to parse it. The OS field and potentially the version and other fields must match the 'os' => and any 'version' => fields in the command_sets.nmis file.
Once you have added the device you will either need to wait for the polling cycles to complete per your cron Schedule or use command line tools below to determine results.
opConfig CLI tools are found in /usr/local/omk/bin
Simply run opconfig-cli.pl without options to see a brief usage of help.
opconfig-cli.pl can import nodes from NMIS, to import you'd run
opconfig-cli.pl act=import_from_nmis ##optionally you can limit it to the names of known nodes with an argument of nodes= opconfig-cli.pl act=import_from_nmis nodes=nodeX,nodeY |
If you have already setup credential sets, then you can let opConfig guess which to use for your node using opconfig-cli.pl act=discover node=TheNewNodeName If none of the Transport+Credential Set combinations work for the node, opconfig-cli.pl will print an error message. |
One can use a cron entry to schedule the opconfig-cli.pl processes as described above, this would import new nodes and update old node information from NMIS on a regular basis.
There are two things to consider when automating this. Firstly the "discover" process which tests for a working combination of the transport (ssh/telnet) and credentials is not recommended for larger numbers of nodes or if have more than about 3 or 4 credential sets to try for obvious reasons. Secondly you may want to apply a filter on which nodes should be considered as Active for opConfig.
One way to automate some of these is to create custom entries in your OS_Rules.nmis. You can use OS_Rules filter and set policies to apply the transport type, the credential set to use and even the enabled or disabled flag.
Here is an example which extends the Cisco IOS section to automatically set the transport and credential sets for all Cisco devices.
10 => {
'IF' => {
'sysDescr' => qr/IOS XR/,
},
'SET' => {
'connection_info.personality' => 'ios',
'os_info.os' => 'IOS-XR',
### These two lines then SET SSH as the transport and the credential_set to use for username and password or SSH keys.
'connection_info.transport' => 'SSH',
'connection_info.credential_set' => 'default_username_password',
### ----
},
'CAPTURE' => [
.........
### One could also set ALL devices to use SSH etc with the following -
## Note: this is rule 1 and does not Break so continues to apply the OS_Rules
1 => {
'IF' => {
'sysDescr' => qr/\S/, ## Matches any sysDescr that is not blank or just a space
},
'SET' => {
'connection_info.transport' => 'SSH',
'connection_info.credential_set' => 'default_username_password',
},
BREAK => 'false',
},
|
| You may also want to use visual panels to communicate related information, tips or things users need to be aware of. |
Related articles appear here based on the labels you select. Click to edit the macro and add or change labels.