...
| Code Block |
|---|
cd script ./opmantek.pl daemon # if that does not give you any errors and runs, CTRL+C and then run ./opmantek.sh # now grep for the opmantek process again, also check the log files in /usr/local/omk/log |
opHA Authentication Model
The opHA daemon is configured with:
- An opHA user and password, by default this is an Apache htpasswd file, defined in /usr/local/omk/conf/users.dat
- The opHA user to use for the authentication, defined per Server in /usr/local/nmis8/conf/Servers.nmis (on the master if they are pulling, for the slaves if they are pushing)
- An IP address list that defines who is allowed to connect to the daemon (depending on the operation a combination of ip address and login credentials is required)
This model enables you to use separate credentials for each slave or the same credentials for each slave, providing for simple configuration, and more secure configuration if required.
opHA Slave Configuration
This configuration will be done on each NMIS Slave Server. By default, the shared community for a slave is "secret" if you want to change this to something specific you can edit the NMIS Configuration item "slave_community" using your favourite text editor, edit this line and change secret to your desired opHA community string.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
'server_community' => 'secret', |
Verify that the Apache user has been configured for master functions. The default userid is "nmismst" and the file /usr/local/nmis8/conf/users.dat should include an entry like
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
nmismst:vnnFthCKoHsps |
opHA Master Configuration
Server Name for opHA
Server names need to be lower case with no spaces, e.g. NMIS_Server24 is bad, nmis_server24 is good.
Adding Slaves to Servers.nmis
Once the slaves have been setup, you can configure the master with each of its slaves. This is done by editing the file /usr/local/nmis8/conf/Servers.nmis, and adding a section for each server.
The default entries look like this:
Enter License and accept EULA
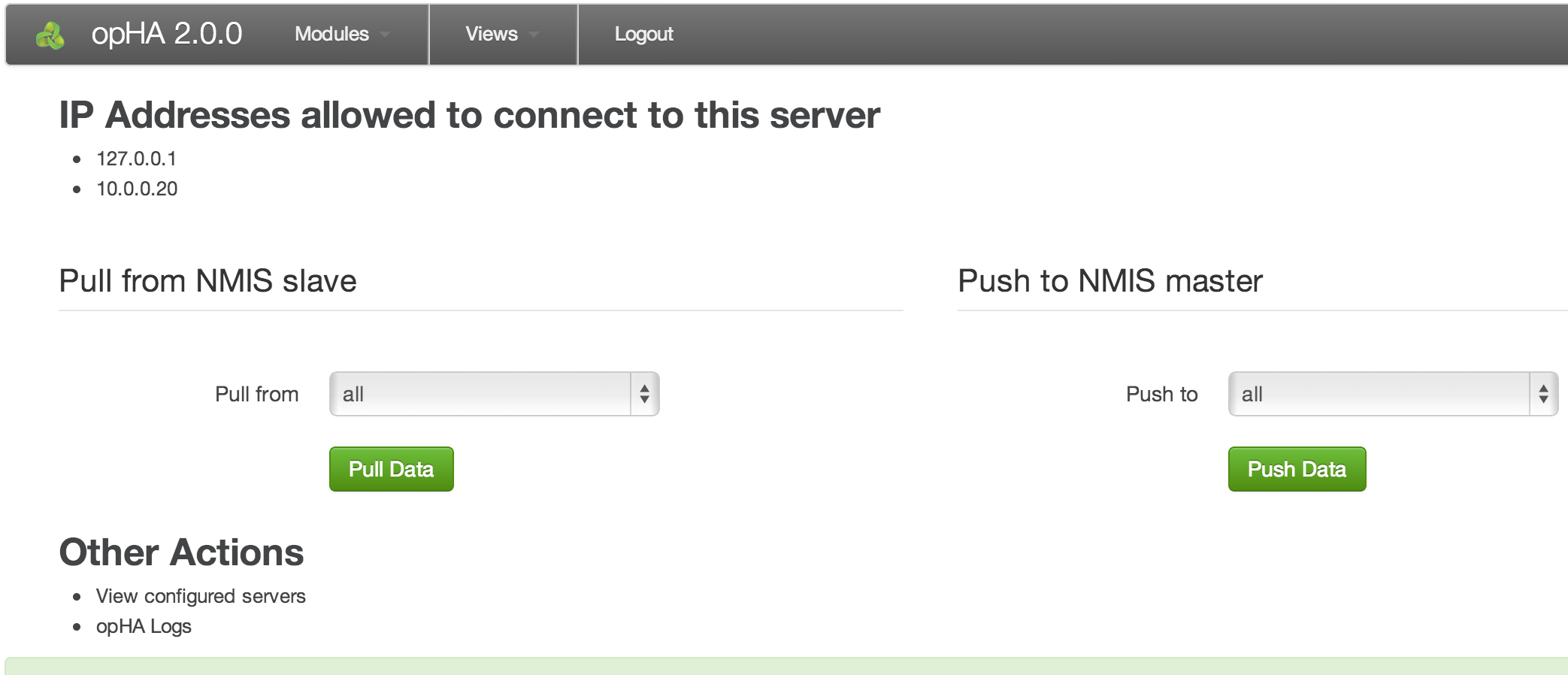
If the daemon is loaded and the installation has gone well you should now be able to load the opHA GUI, from http://server_name:3000/opHA. This URL should present you with a webpage that allows you to enter a license key and accept a EULA. This step will need to be completed on each opHA instance. After successful license key and EULA acceptance you will be presented with a dashboard that looks like this:
opHA Authentication Model
The opHA daemon is configured with:
- An opHA user and password, by default this is an Apache htpasswd file, defined in /usr/local/omk/conf/users.dat
- The opHA user to use for the authentication, defined per Server in /usr/local/nmis8/conf/Servers.nmis (on the master if they are pulling, for the slaves if they are pushing)
- An IP address list that defines who is allowed to connect to the daemon (depending on the operation a combination of ip address and login credentials is required)
This model enables you to use separate credentials for each slave or the same credentials for each slave, providing for simple configuration, and more secure configuration if required.
- To add new users see the documentation here for adding users to htpasswd
- After you have the users configured you will need to modify conf/opCommon.nmis, find the line "'opha_allowed_ips' => ['127.0.0.1'] and add the IP addresses of the opHA servers that are allowed to connect to the server you are configuring.
For example, if we want to allow the servers at 192.168.1.42 and 192.168.2.42 to connect to this server, we add them to conf/opCommon.nmis like this:
| Code Block |
|---|
'opha_allowed_ips' => ['127.0.0.1', '192.168.1.42', '192.168.2.42'], |
opHA Configuration
Server Name for opHA
Server names need to be lower case with no spaces, e.g. NMIS_Server24 is bad, nmis_server24 is good.
Add Servers to Servers.nmis
opHA supports slaves pushing updates or masters pulling updates (or both). If you want a slave to have the ability to push, it needs to have the servers it should push to in it's Servers.nmis file. Conversely if you want masters to be able to pull they need to have the slaves they should pull from in their Servers.nmis file. At this point it is good to draw yourself a diagram (if you have not already) to aid you in configuring each master and slave.
In addtion: each server (master and slave) needs to have a localhost entry which tells the server how to log in to itself.
The Servers nmis file is located at /usr/local/nmis8/conf/Servers.nmis, you will need to add a section for each server the daemon will be connecting to. The NMIS GUI can help you create these entries.
The default entries look like this:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
'nmis1' => {
'community' => 'secret', # this is unused
'name' => 'nmis1', # what to name this server in the GUI
'config' => 'Config.nmis',
'protocol' => 'https',
'port' => '443', # this should be 3000, the port that omkd runs on
'host' => 'nmis1.domain.com', # the name/ip address omkd will use to connect to the server
'portal_protocol' => 'http', # the next entries define how links in the master will appear, these can be ignored for master entries on slave omkd's
'portal_ | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
'nmis1' => { 'community' => 'secret', 'name' => 'nmis1', 'config' => 'Config.nmis', 'protocol' => 'https', 'port' => '443', 'host' => 'nmis1.domain.com', 'portal_protocol' => 'http', 'portal_port' => '80', 'portal_host' => 'nmis1.alternate.com', 'cgi_url_base' => '/cgi-nmis8', 'url_base' => '/nmis8', 'user' => 'nmismst', 'passwd' => 'C00kb00k' }, 'nmis2' => { 'community' => 'secret', 'name' => 'nmis2', 'config' => 'Config.nmis', 'protocol' => 'http', 'port' => '80', 'portal_host' => '192nmis1.168alternate.1.42com', 'portalcgi_url_protocolbase' => 'http/cgi-nmis8', 'portalurl_portbase' => '80/nmis8', 'portal_hostuser' => 'nmis2nmismst', # 'cgi_url_base' => '/cgi-nmis8', 'url_base' => '/nmis8',the user omkd will connect to this server with 'userpasswd' => 'nmismstC00kb00k', # the 'passwd' => 'C00kb00k' } |
Edit the entry to look like this, in this example the hostname of the slave is "vali":
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
'valipassword omkd will connect to this server with }, 'nmis2' => { 'community' => 'YOURNAMEHEREsecret', 'name' => 'valinmis2', 'config' => 'Config.nmis', 'protocol' => 'http', 'port' => '80', 'host' => 'vali192.168.1.42', 'portal_protocol' => 'http', 'portal_port' => '80', 'portal_host' => 'valinmis2', 'cgi_url_base' => '/cgi-nmis8', 'url_base' => '/nmis8', 'user' => 'nmismst', 'passwd' => 'C00kb00k' } |
There are many options in this configuration but unless you are wanting to change the defaults considerably most of them will not matter. If you wanted to use HTTPS to connect between the master and the slave, you could use https as the protocol and update the port accordingly. You can use different user and passwd permissions here.
If you were presenting the Slave and needed to use an alternate connection, e.g. through a reverse proxy for presenting a portal, you would modify the portal_protocol, portal_port and portal_host accordingly.
Promoting NMIS to be a Master
By default, an NMIS server operates in standalone mode (which is also slave mode), to have NMIS behave in a masterly fashion, you will need to modify the configuration, so you can edit the NMIS Configuration item "sever_master" using your favourite text editor, edit this line and change from "false" to "true".
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
'server_master' => 'true', |
Adding Slave Groups to Master
On each slave you will need to determine which groups are currently in use.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
[root@vali conf]# grep group_list /usr/local/nmis8/conf/Config.nmis
'group_list' => 'HQ,HQDev', |
This will result in a list of groups which need to be added to the NMIS Master, edit /usr/local/nmis8/conf/Config.nmis and add these groups to that list, this is a comma separated list.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
'group_list' => 'NMIS8,DataCenter,Branches,Sales,Campus,HeadOffice,HQ,HQDev', |
Limiting Master Group Collection
opHA supports Multi-Master, that means you can have several masters collecting information from the same slaves if required. This could be especially useful if you wanted to have one master with all groups on a slave, and another master with different groups from different slaves, effectively sharing some information between groups.
To do this you use the group property in the Servers.nmis file. Edit the file and add the group property in and a regular expression in for the groups, this will take the form
| Code Block |
|---|
'group' => 'Brisbane|Boston|Saratoga', |
This will match all groups contain the sub-strings, Brisbane, Boston or Saratoga. A complete server entry would look like this.
| Code Block |
|---|
'demo' => {
'community' => 'secret',
'name' => 'demo',
'config' => 'Config',
'protocol' => 'http',
'port' => '80',
'host' => '192.168.1.42',
'group' => 'Brisbane|Boston|Saratoga',
'portal_protocol' => 'http',
'portal_port' => '80',
'portal_host' => 'demo.dev.opmantek.com',
'cgi_url_base' => '/cgi-nmis8',
'url_base' => '/nmis8',
'user' => 'nmismst',
'passwd' => 'C00kb00k'
}, |
Test Master Collection
You can verify if the master is collecting data from the slaves by running this command
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
[root@thor conf]# /usr/local/nmis8/bin/nmis.pl type=master debug=true sleep=1
NMIS Copyright (C) 1999-2011 Opmantek Limited (www.opmantek.com)
This program comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY;
This is free software licensed under GNU GPL, and you are welcome to
redistribute it under certain conditions; see www.opmantek.com or email
contact@opmantek.com
NMIS version 8.3.4G
14:00:33 nmisMaster, Running NMIS Master Functions
14:00:33 nmisMaster, Master, processing Slave Server vali
14:00:33 nmisMaster, Get loadnodedetails from vali
14:00:33 nmisMaster, Get sumnodetable from vali
14:00:34 nmisMaster, get summary8 from vali
14:00:34 nmisMaster, get summary16 from vali
[root@thor conf]#
|
Running a Master Collection
You can optionally have the NMIS polling cycle do the master collection, or you can run it separately from Cron. If you want to have it seperate which is a good option, change the following NMIS configuration item nmis_master_poll_cycle to be false in the file /usr/local/nmis8/conf/Config.nmis:
| Code Block |
|---|
'nmis_master_poll_cycle' => 'false', |
Then add this line to the crontab which runs your nmis collections.
| Code Block |
|---|
*/2 * * * * /usr/local/nmis8/bin/nmis.pl type=master |
Edit the entry to look like this, in this example the hostname of the slave is "vali":
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
'vali' => {
'community' => 'can_be_empty',
'name' => 'vali',
'config' => 'Config.nmis',
'protocol' => 'http',
'port' => '3000',
'host' => 'vali',
'portal_protocol' => 'http',
'portal_port' => '80',
'portal_host' => 'vali',
'cgi_url_base' => '/cgi-nmis8',
'url_base' => '/nmis8',
'user' => 'nmismst',
'passwd' => 'C00kb00k'
} |
There are many options in this configuration but unless you are wanting to change the defaults considerably most of them will not matter. Currently using HTTPS is not supported in the protocol section. You can use different user and passwd permissions here.
If you were presenting the Slave and needed to use an alternate connection, e.g. through a reverse proxy for presenting a portal, you would modify the portal_protocol, portal_port and portal_host accordingly.
Testing Server Connections
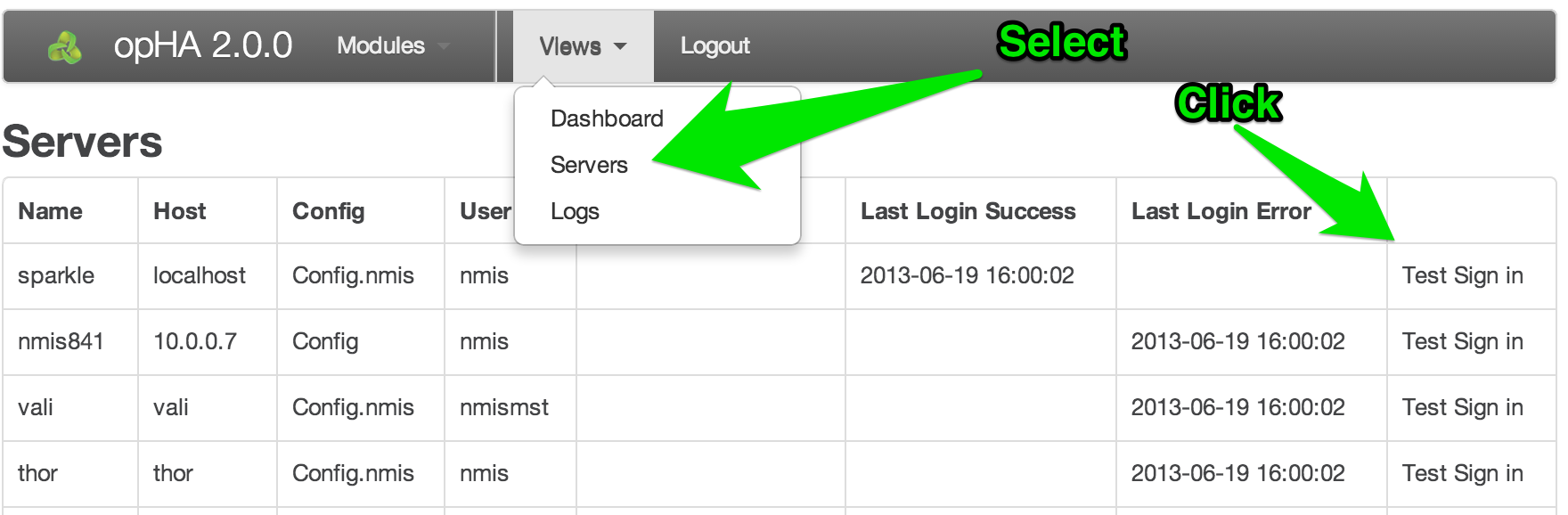
Load the opHA dashboard (http://server_name:3000/opHA/) and from the top menu, select "Views" and then "Servers". You should now be presented with a list of servers that you have configured for this opHA instance. There will be a column with links named "Test Sign In", select the server you would like to test, on successful sign in you will be presented with a page that says "Login Success". If you do not see this you will get an error giving you a hint at what is happening. You can use the logs in /usr/local/omk/log to help you determine what the issue is.
Refreshing the servers page after a successful signin will show the date of the last successful signin (as well as the last login error and last update).
Promoting NMIS to be a Master
By default, an NMIS server operates in standalone mode (which is also slave mode), to have NMIS behave in a masterly fashion, you will need to modify the configuration, so you can edit the NMIS Configuration item "sever_master" using your favourite text editor, edit this line and change from "false" to "true".
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
'server_master' => 'true',
'nmis_master_poll_cycle' => 'false' # this must be false |
Adding Slave Groups to Master
On each slave you will need to determine which groups are currently in use.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
[root@vali conf]# grep group_list /usr/local/nmis8/conf/Config.nmis
'group_list' => 'HQ,HQDev', |
This will result in a list of groups which need to be added to the NMIS Master, edit /usr/local/nmis8/conf/Config.nmis and add these groups to that list, this is a comma separated list.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
'group_list' => 'NMIS8,DataCenter,Branches,Sales,Campus,HeadOffice,HQ,HQDev', |
Limiting Master Group Collection
opHA supports Multi-Master, that means you can have several masters collecting information from the same slaves if required. This could be especially useful if you wanted to have one master with all groups on a slave, and another master with different groups from different slaves, effectively sharing some information between groups.
To do this you use the group property in the Servers.nmis file. Edit the file and add the group property in and a regular expression in for the groups, this will take the form
| Code Block |
|---|
'group' => 'Brisbane|Boston|Saratoga', |
This will match all groups contain the sub-strings, Brisbane, Boston or Saratoga. A complete server entry would look like this.
| Code Block |
|---|
'demo' => {
'community' => 'secret',
'name' => 'demo',
'config' => 'Config',
'protocol' => 'http',
'port' => '80',
'host' => '192.168.1.42',
'group' => 'Brisbane|Boston|Saratoga',
'portal_protocol' => 'http',
'portal_port' => '80',
'portal_host' => 'demo.dev.opmantek.com',
'cgi_url_base' => '/cgi-nmis8',
'url_base' => '/nmis8',
'user' => 'nmismst',
'passwd' => 'C00kb00k'
}, |
Test Push/Pull
There are several ways to verify that the transfers are working correctly:
- use the GUI to do a pull or push (http://server_name:3000/opHA/), select the server you want to push to or pull from (or select all to test them all) and press the appropriate button
the output will be a JSON document, with a hash entry for each successful file transfer:
Code Block { source: "vali", success: "Transfer complete", file_name: "nmis-summary8h", destination: "localhost" },On error there will be a hash entry with an error key along with information to help you solve the problem
Code Block { url: "http://vali:443/login", error: "Error signing in", server_signin_url: "http://localhost:3000/opHA/servers/vali/signin", message: "Transaction was not a success.", server_name: "vali" },
- check the logs and watch the transfers happen
- view the list of configured servers and check the "Last Update" column
Running a Master Collection
There are two options to run opHA, using Cron or a as a post process after a NMIS does a collect. Pushes and pulls can be requested from anywhere, if they are requested from the localhost no authentication is required, if they are requested from elsewhere authentication is required.
Before you start make sure you have this in Config.nmis
| Code Block |
|---|
'nmis_master_poll_cycle' => 'false', |
To run from cron add this line to the crontab which runs your nmis collections. This line will push or pull (depending on which one you pick) to all servers. If you would only like to push or pull to a specific server replace "all" with the server name
| Code Block |
|---|
*/2 * * * * wget http://localhost:3000/opHA/servers/all/[push|pull] -o /dev/null# all servers
*/2 * * * * wget http://localhost:3000/opHA/servers/vali/pull -o /dev/null # just pull server vali |
This will get your collections running every 2 minutes regardless of other polling.
To run after an NMIS collect, put a script like this in /usr/local/nmis8/bin/nmis_post_proc.pl
| Code Block |
|---|
package pp;
require 5;
use strict;
sub doPP {
system("curl -s http://localhost:3000/opHA/servers/all/pull");
system("wget http://localhost:3000/opHA/servers/all/pull -o /dev/null");
return 1;
}
|
Logs
Logs can be found in /usr/local/omk/log or also viewed from the GUI at http://server_name:3000/opHA/logsThis will get your collections running every 2 minutes regardless of other polling. There is also an option called master_sleep which is so that your type=update and type=master can run every 1 minute and still have data, the default offset is 15.
Conclusion
After refreshing the web pages on the NMIS Master server you will see the data from the slaves.