...
| Code Block |
|---|
\HKEY_USERS\.DEFAULT\Software\Microsoft\Windows Script\Settings |
DCOM
Run the DCOM utility and verify (or set) the below attributes. Start -> Run, Enter DCOMCNFG and press OK. This will open the DCOMCNFG window.
Browse down the tree to Console Root -> Component Services -> Computers -> My Computer
Right click on "My Computer" and select properties
Select the "Default Properties" tab
- Enable Distributed COM on this computer - Option is checked
- Default Authentication Level - Set to Connect
- Default Impersonation Level - Set to Identify
Select the "COM Security" tab
Click on Access Permissions ' Edit Default
- Add "Anonymous", "Everyone", "Interactive", "Network", "System" with Local and Remote access permissions set.
Click on Launch and Activation Permissions ' Edit Default
- Add "Anonymous", "Everyone", "Interactive", "Network", "System" with Local and Remote access permissions set.
Click on OK and close the DCOMCNFG window.
The above changes will require a reboot to take effect.
UAC
If you are getting an Access Denied scan error it might be UAC blocking inbound requests on the remote device. If the remote computer you are trying to query is in a workgroup (or not joined to a domain), UAC prevents remote queries by default, even if the account being used is in the Administrators group. Completely disabling UAC on the remote device allows you to get around this, but it is preferable to disable the subcomponent of UAC instead. You can do this by adding or editing this registry key on the remote device you are scanning and setting its value to 1:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy
Note that Windows 8 and Server 2012 do not have a way to completely disable UAC (adjusting the slider in the GUI just disables notifications). You'll need to use the registry key method.
You can use this command from a command prompt on the remote device to quickly add the registry key:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f |
Reference - https://support.microsoft.com/kb/942817
Enabling the Administrator account on non-Domained machines
Open a command prompt with administrative rights (Windows key, type 'cmd' (sans quotes) right click Command Prompt and select Run as Administrator.
In the command window type
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
net user Administrator |
You should see Active set to false. Enable it with
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
net user Administrator /active:yes |
Then run the first command again and confirm Active is now set. Then set the password with:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
net user Administrator * |
And type 'exit' to close the window.
Windows 7 and 2008 R2 not submitting audit using HTTPS
We have been advised that some Windows 7 and Windows 2008 R2 machine will not submit their audit result to the Open-AudIT server when running HTTPS. If this affects you , please see the following Microsoft article - https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/3140245/update-to-enable-tls-1-1-and-tls-1-2-as-default-secure-protocols-in-wi
DCOM
Run the DCOM utility and verify (or set) the below attributes. Start -> Run, Enter DCOMCNFG and press OK. This will open the DCOMCNFG window.
Browse down the tree to Console Root -> Component Services -> Computers -> My Computer
Right click on "My Computer" and select properties
Select the "Default Properties" tab
- Enable Distributed COM on this computer - Option is checked
- Default Authentication Level - Set to Connect
- Default Impersonation Level - Set to Identify
Select the "COM Security" tab
Click on Access Permissions ' Edit Default
- Add "Anonymous", "Everyone", "Interactive", "Network", "System" with Local and Remote access permissions set.
Click on Launch and Activation Permissions ' Edit Default
- Add "Anonymous", "Everyone", "Interactive", "Network", "System" with Local and Remote access permissions set.
Click on OK and close the DCOMCNFG window.
The above changes The above change will require a reboot to take effect.
Local Security Policies
Run one of the following three Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-ins:
- the Local Security Policy snap-in (secpol.msc) for member servers, or
- the Default Domain Security Policy snap-in (dompol.msc) if you wish to configure these settings domain-wide as a GPO, or
- the Default Domain Controller Security Settings snap-in (dcpol.msc) if you wish to assign the rights only on domain controllers.
Expand Security Settings -> Local Policies -> User Rights Assignment.
Check the Administrators Group has at least the following rights:
- Act as part of the operating system
- Log on as a batch job
- Log on as a service
- Replace a process level token
Go to Start -> Control Panel -> Administrative Tools -> Local Security Policy
Navigate to Security\Local Policies\Security Options
- DCOM: Machine Access Restrictions - Add Anonymous, Everyone, Interactive, Network, System with full rights options set.
- Network Access: Let everyone permissions apply to anonymous users - Set to Enabled
- Network Access: Sharing security model for local accounts - Set to Classic
- User Account Control: Run all Administrators in Admin Approval Mode - Set to Disabled
The above changes will require a reboot to take effect.
Simple File Sharing (XP)
Windows XP Professional computers in a workgroup environment will need simple file sharing disabled. You can make this change through the registry by setting the following key to a value of 0.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\ForceGuest
If this key does not exist, you can add it using a command prompt by:
UAC
If you are getting an Access Denied scan error it might be UAC blocking inbound requests on the remote device. If the remote computer you are trying to query is in a workgroup (or not joined to a domain), UAC prevents remote queries by default, even if the account being used is in the Administrators group. Completely disabling UAC on the remote device allows you to get around this, but it is preferable to disable the subcomponent of UAC instead. You can do this by adding or editing this registry key on the remote device you are scanning and setting its value to 1:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy
Note that Windows 8 and Server 2012 do not have a way to completely disable UAC (adjusting the slider in the GUI just disables notifications). You'll need to use the registry key method.
You can use this command from a command prompt on the remote device to quickly add the registry key:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System /v LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy / | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa /v ForceGuest /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f |
You can also do this through settings by performing the following steps:
Click Start → Control Panel → Folder Options.
Select the View tab and scroll to the bottom of the Advanced Settings: section.
Uncheck the Use simple file sharing (Recommended) to disable the option and click the OK button.
SSPI means Security Support Provider Interface and is the interface used by VBscript / WMI to validate the user.
- If ForceGuest is enabled (set to 1), SSPI will always try to log on using the Guest account.
- If the Guest account is enabled, an SSPI logon will succeed as Guest for any user credentials.
- If the Guest account is disabled, an SSPI logon will fail even for valid credentials.
- If ForceGuest is disabled (set to 0), SSPI will log on as the specified user.
The above changes will require a reboot to take effect.
WMI
Windows WMI (Windows Management Interface) is used by the audit script for most of it's information retrieval. WMI can (at times) become corrupted. Microsoft have released a tool to enable you to check for this corruption.
The tool is available from Microsoft, here - http://www.microsoft.com/en-au/download/details.aspx?id=7684
Using the tool is detailed here - http://blogs.technet.com/b/askperf/archive/2012/02/03/wmidiag-2-1-is-here.aspx
1 /f |
Reference - https://support.microsoft.com/kb/942817
The above change will require a reboot to take effect.
Local Security Policies
Run one of the following three Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-ins:
- the Local Security Policy snap-in (secpol.msc) for member servers, or
- the Default Domain Security Policy snap-in (dompol.msc) if you wish to configure these settings domain-wide as a GPO, or
- the Default Domain Controller Security Settings snap-in (dcpol.msc) if you wish to assign the rights only on domain controllers.
Expand Security Settings -> Local Policies -> User Rights Assignment.
Check the Administrators Group has at least the following rights:
- Act as part of the operating system
- Log on as a batch job
- Log on as a service
- Replace a process level token
Go to Start -> Control Panel -> Administrative Tools -> Local Security Policy
Navigate to Security\Local Policies\Security Options
- DCOM: Machine Access Restrictions - Add Anonymous, Everyone, Interactive, Network, System with full rights options set.
- Network Access: Let everyone permissions apply to anonymous users - Set to Enabled
- Network Access: Sharing security model for local accounts - Set to Classic
- User Account Control: Run all Administrators in Admin Approval Mode - Set to Disabled
The above changes will require a reboot to take effect.
Simple File Sharing (XP)
Windows XP Professional computers in a workgroup environment will need simple file sharing disabled. You can make this change through the registry by setting the following key to a value of 0.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\ForceGuest
If this key does not exist, you can add it using a command prompt by:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa /v ForceGuest /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f |
You can also do this through settings by performing the following steps:
Click Start → Control Panel → Folder Options.
Select the View tab and scroll to the bottom of the Advanced Settings: section.
Uncheck the Use simple file sharing (Recommended) to disable the option and click the OK button.
SSPI means Security Support Provider Interface and is the interface used by VBscript / WMI to validate the user.
- If ForceGuest is enabled (set to 1), SSPI will always try to log on using the Guest account.
- If the Guest account is enabled, an SSPI logon will succeed as Guest for any user credentials.
- If the Guest account is disabled, an SSPI logon will fail even for valid credentials.
- If ForceGuest is disabled (set to 0), SSPI will log on as the specified user.
The above changes will require a reboot to take effect.
WMI
Windows WMI (Windows Management Interface) is used by the audit script for most of it's information retrieval. WMI can (at times) become corrupted. Microsoft have released a tool to enable you to check for this corruption.
The tool is available from Microsoft, here - http://www.microsoft.com/en-au/download/details.aspx?id=7684
Using the tool is detailed here - http://blogs.technet.com/b/askperf/archive/2012/02/03/wmidiag-2-1-is-here.aspx
For Windows Core servers, ensure you allow the firewall connections as per - http://blogs.technet.com/b/brad_rutkowski/archive/2007/10/22/unable-to-remotely-manage-a-server-core-machine-mmc-wmi-device-manager.aspx
Networking with WMI
By default, Windows sends WMI data over random ports, as explained in this Microsoft knowledge base article. You need to either:
• Configure your firewalls in such a way that all WMI traffic (over random ports) is allowed. Windows Firewall includes a remote administration exception that you can enable to allow WMI traffic, as explained in this knowledge base article. For third-party firewalls, you'll need to consult your firewall documentation.
• Configure a fixed WMI port and allow traffic through that port. Setting up a fixed port is supported by Windows Vista and more recent operating systems.
Testing Remote WMI
When testing remote WMI you should disable the Windows Firewall, Antivirus, and UAC. Test as below. If it succeeds, begin by enabling one of the disabled items at a time, test and if it works, enable the next item. If any failed connections occur, it is likely the component you have just enabled. Fix that component and try again.
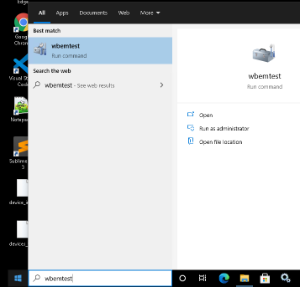
To test WMI remote network connections.
- RDP to the another Windows machine (if running Open-AudIT on Linux), or if you're running Open-AudIT on Windows, the Open-AudIT server.
- Click Start menu, then type: wbemtest
- Open the utility.
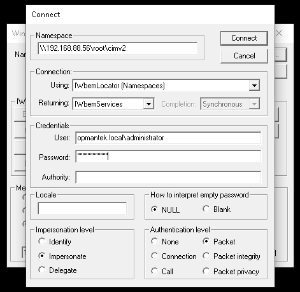
- Click Connect...
- Enter the information
- Within namespace, type: \\TARGET_DEVICE_IP\root\cimv2 - where TARGET_DEVICE_IP is the IP of the device not being discovered by Open-AudIT.
- For the Username, use the format domain\username
- Enter the password
- Leave the Authority field blank.
- Click connect
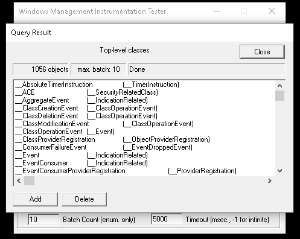
- Click Enum Classes and select Recursive, then click OK
- It may take several seconds to respond.
- If it does not work, the target PC has an issue (or something between the target PC and Open-AudIT).
- if it does work, please log a support ticket with Opmantek.
Testing Remote WMI #2
Open a command prompt and try the following command. Substitute your domain, username, password and target IP.
You should get a result similar to the below.
NOTE - the extra r's and for the (r) registered trademark symbols, no need to be concerned with them.
| Code Block |
|---|
C:\Users\opDev>wmic /user:YOUR_DOMAIN\YOUR_USERNAME /password:YOUR_PASSWORD /node:YOUR_IP os get name
Name
Microsoftr Windows Serverr 2008 Enterprise |C:\Windows|\Device\Harddisk0\Partition1 |
If the response is: Description: RPC Server is unavailable, then you have a firewall or other issue.
If the response is: Description: Access Denied Facility = Win32 then the credentials that were supplied don't have Windows DCOM permissions on the Target machine.
If the response is: Description: Access denied Facility = WMI then the credentials that were supplied don't have WMI Security permissions on the Target machine.
Matching Discovery Logs to WMI issues
If you see the below, try the following fixes.
ERROR: Failed to open connection - NT_STATUS_LOGON_FAILURE
Check your credentials and that they are of a machine Administrator account.
ERROR: Failed to open connection - NT_STATUS_CONNECTION_RESET
Likely from our attempt to use SMB1, which the target Windows PC no longer accepts.
ERROR: Failed to save ADMIN$/winexesvc.exe - NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED.
Are the ADMIN$ and IPC$ shares enabled? Check as below.
ERROR: UploadService failed - NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED.
Are the ADMIN$ and IPC$ shares enabled? Check as below.
ERROR: Failed to install service winexesvc - NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
This most likely means the user account being used does not have sufficient rights on the target machine. To fix this issue, see the section above on this page for UAC.
ERROR: StartService Failed - NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
We are still investigating possible causes for this issue. It appears that the winexesvc.exe file has been copied to the target and the service registered, however it fails to start. This may be Antivirus related. We are unsure at this stage.
Winexe requirements (Linux only) on Windows machines
Enabled services: Workstation, Server.
"Windows Network" is running and "Printer and File Sharing" are activated.
Enabled "Remote IPC" and "Remote Admin" shares. To verify it, in cmd box run command "net share", and check if there are ADMIN$ and IPC$ shares.
An account with administrative privileges and not empty password. If Windows machine is not on a domain, it is best to use the Administrator account (see above).
Firewall rules allowing traffic between both machines.For Windows Core servers, ensure you allow the firewall connections as per - http://blogs.technet.com/b/brad_rutkowski/archive/2007/10/22/unable-to-remotely-manage-a-server-core-machine-mmc-wmi-device-manager.aspx
AntiVirus
Some antivirus programs have been known to disable DCOM and remote WMI. You might check the settings of your antivirus program and disable them for testing. We recently had a report of Trend AV specifically blocking calls to winexesvc when auditing Windows computers.
...