Compatible with NMIS9
Tabled of Contents
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Introduction
...
Quickstart Chart of a Service Definition
| Parameter Name | Relevant for which Service Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
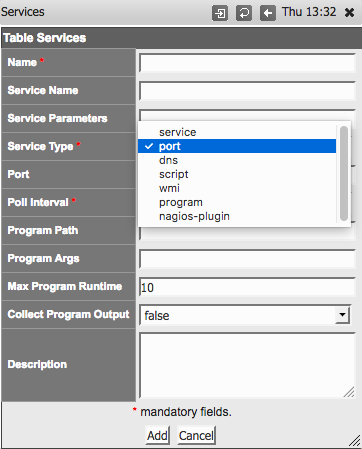
| Name | all | Every service definition must have a unique service name. In NMIS |
versions before 8.6.2 this also sets the script name for type script. | ||
| Service_Type | all | Every service must specify the type of check to perform. |
| Description | all | optional, free from text |
| Service_Name | service, |
|
| Service_Parameters | service | Regular expression to match by executable path and process arguments |
| Poll_Interval | all except service | SNMP-based services are only checked during a type=collect poll cycle |
| Port | port and | port: The TCP or UDP Port number to perform a connect check on.script: The TCP port to perform scripted communication on on. |
| Program | program and nagios-plugin | The external program or plugin that performs the actual service test |
| Args | program and nagios-plugin | The arguments for that external program |
| Max_Runtime | program and nagios-plugin | How long to let that program run at most |
| Collect_Output | program and nagios-plugin | Whether the program output should be collected and stored |
...
Configuring NMIS to Monitor Services - Step By Step
...
This is how to define a new services based on using SNMP for the status of the service.
This feature requires the device to support the HOST-RESOURCES-MIB, and specifically the hrSWRun instrumentation which provides "The (conceptual) table of software running on the host."
Step 1
Determine the name of the service process you want to monitor, for example to Monitor MongoDB on Windows, the process name is mongod.exe. As the MongoDB server state is reported as an attribute for the named process, you'll have to tell NMIS what process to look for.
...
For example, if you want to check a particular Java application, you would set the Service Name to java and the Service Parameters to some identifying property for this particular application. To figure out what exactly might distinguish this application from others, have a look at the Service List page for that node, and the Service and Parameters columns in particular:
| Service | Parameters |
|---|---|
| java | -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/opt/confluence/conf/logging.properties -Xms512m -Xmx768m -XX:MaxPermSize=512m -Djava.awt.headle |
| mingetty | /sbin/mingetty /dev/tty2 |
In this example, the Java process happens to be the one for the Confluence application, and the mingetty is the one covering the second terminal.
...
Assuming you only want to check if a server listens for network connections on a particular TCP or UDP port (without actually exchanging application-level data with that service), then this is how to instruct NMIS to do that:
- Select Service Type
port - Give the appropriate port and protocol in the form of
udp:123(that would be NTP) ortcp:22(that's SSH) - Ignore Service Name and all program-related settings
...
- Service Type is
dns. - Up to version 8.4.10G inclusive, the builtin dns monitor requires the node's Name/IP Address setting to hold the node's fully qualified domain name. NMIS then requests DNS info for this FQDN from the node that is marked for dns service monitoring. The Service Name is ignored.
- After version 8.4.10G, you have to specify what is to be looked up must specify the DNS query target as the Service Name. This can be either an IP address or a fully qualified domain name (host or domain). Again it is the node marked for dns monitoring that is asked for DNS info, but you've got control over what is requested.
...
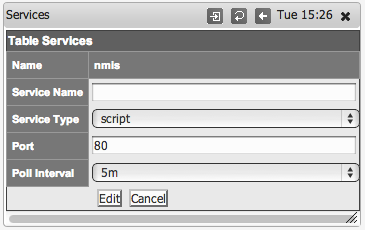
Then select add or edit to add a new service or edit an existing service monitoring definition.
Step 4
Give the service a name, in this example "nmis", and declare it to be of type script and define the port - here port 80.
In NMIS 8.6.2 and newer you must set the script name in the "Service Name" property; in versions before that the "Name" also controlled the script name.
...