...
With the 3.3.0 release of Open-AudIT we have introduced the concept of a Cluster. This intuitively maps to the idea of a web, database, file (or one of several other typespurposes) cluster in a given type (high availability, redundancy, scaling, etc).
Depending on the type purpose of cluster chosen, the reporting will be slightly different.
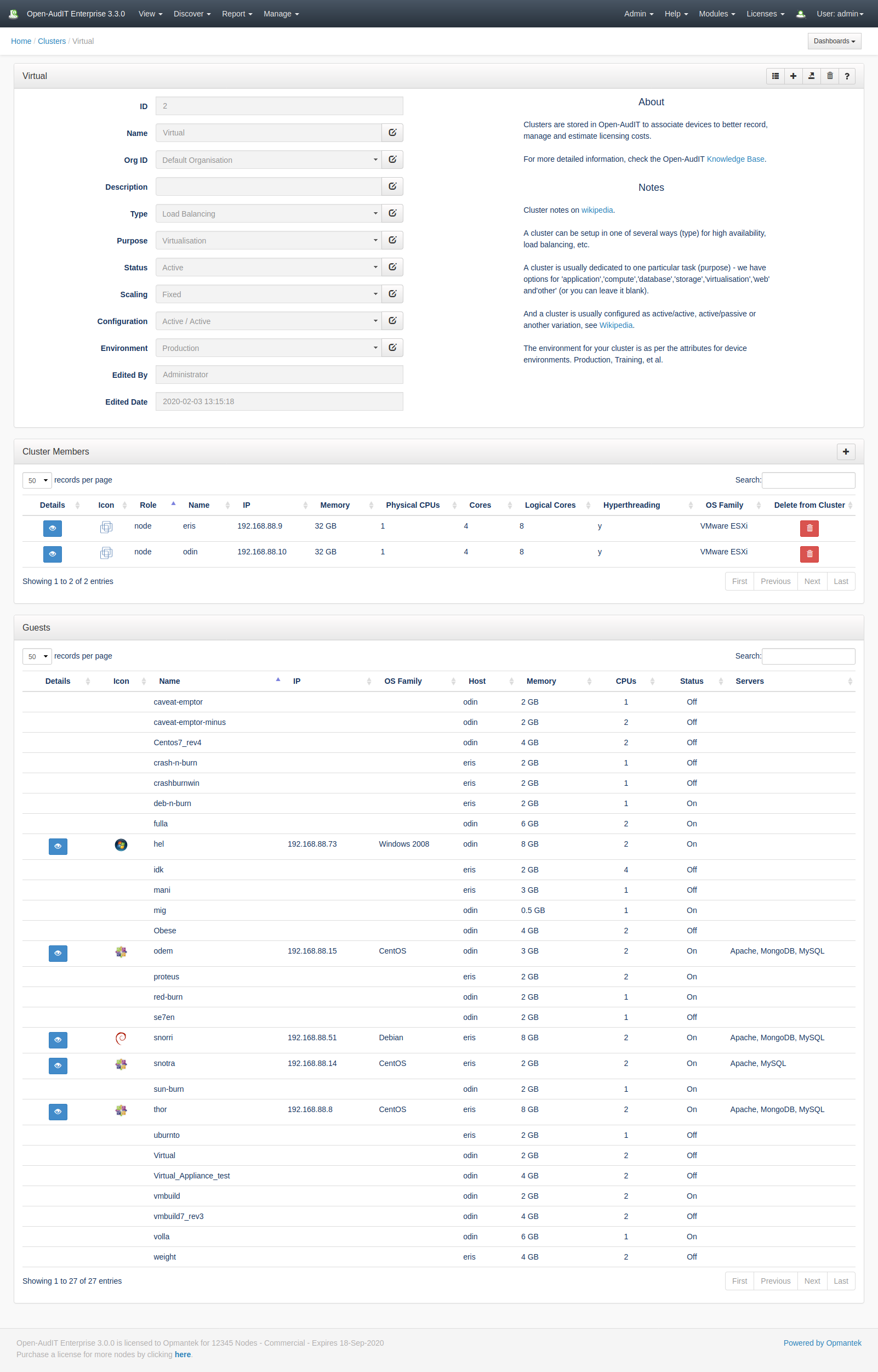
For example, if you create a Cluster with a purpose of virtualisation, when you have added devices to it you will also see the virtual machines on those devices. An example is below.
Clusters are just another collection, like any other. An entry for them in Roles-Permissions has been created. You can Create, Read, Update and Delete them using the API like any other collection.
In the future we hope to be able to automatically detect Microsoft SQL and File clusters along with ESXi clusters.
Database Schema
| Code Block |
|---|
CREATE TABLE `clusters` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`org_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '1',
`description` text NOT NULL,
`type` enum('high availability','load balancing','performance','storage','other','') NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`purpose` enum('application','compute','database','storage','virtualisation','web','other','') NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`status` enum('active','inactive','other','') NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`configuration` enum('active/active','active/passive','N+1','N+M','N-to-1','N-to-N','other','') NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`environment` varchar(100) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'production',
`scaling` enum('auto','fixed','other','') NOT NULL DEFAULT 'fixed',
`retrieved_name` varchar(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`retrieved_ident` varchar(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`edited_by` varchar(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`edited_date` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT '2000-01-01 00:00:00',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; |
And the table that stores the cluster ↔ device relationships.
In this regard, it's similar to the files and file tables and their relationship.
| Code Block |
|---|
CREATE TABLE `cluster` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`system_id` int(10) unsigned DEFAULT NULL,
`clusters_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
`role` enum('head','node','storage','network','other','') NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`current` enum('y','n') NOT NULL DEFAULT 'y',
`edited_by` varchar(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
`edited_date` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT '2000-01-01 00:00:00',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `system_id` (`system_id`),
KEY `cluster_clusters_id` (`clusters_id`),
CONSTRAINT `cluster_clusters_id` FOREIGN KEY (`clusters_id`) REFERENCES `clusters` (`id`) ON DELETE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT `cluster_system_id` FOREIGN KEY (`system_id`) REFERENCES `system` (`id`) ON DELETE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; |
Example database entry
...
Database Schema
The database schema can be found in the application is the user has database::read permission by going to menu: Admin -> Database -> List Tables, then clicking on the details button for the table.
API / Web Access
You can access the
...
collection using the normal Open-AudIT JSON based API. Just like any other collection. Please
...
see The Open-AudIT API documentation for further details
...
API Routes
...
.
...
Web Application Routes
...