...
- Checks Host Resources MIB for service status
- Performs poll of TCP/UDP port
- Runs a script which returns send/expect scripts which return status (can perform full transaction over system and is highly extensible)
- Run external programs which return status (and optionally extra values)
You can download NMIS from the Opmantek webpage.
...
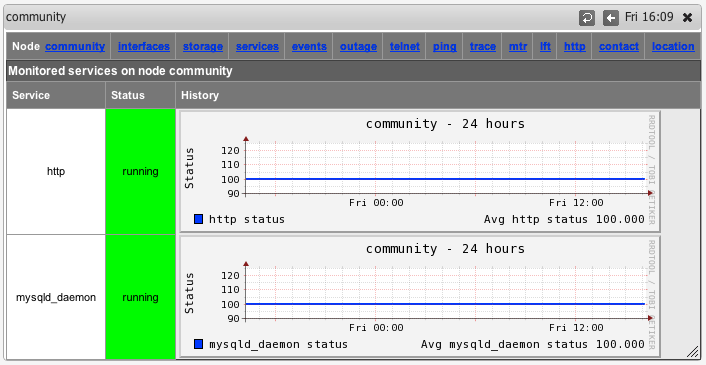
You can also now select "Services" from the node menu bar and see a graph of all the monitored services.
From version 8.4.10G onwards the service graphs also include the response time (as number and and graph) which is the elapsed time of the service test.
Defining new SNMP based Services to Monitor
...
This is how to define a new services based on using a sapi script to connect to the socket and send some data, looking for the correct response.
Sapi scripts are extremely similar to expect scripts and documented at the end of /usr/local/nmis8/lib/sapi.pm.
Step 1
Determine the name of the service you want to monitor, for example to is the NMIS web application running.
...
Step 5
Create a script which will get to the appropriate WEB Application URL, use the basic http service as a basis, the name of the service will be the name of the script
| Code Block |
|---|
cp /usr/local/nmis8/conf/scripts/http /usr/local/nmis8/conf/scripts/nmis |
Then edit that script and change the script to get your URL correctly, in this example the final nmis script looked like this:
| Code Block |
|---|
send: HEAD /nmis8/ HTTP/1.0 send: expect: 200 OK |
So this script will connect to port 80, send the "HEAD /nmis8/ HTTP/1.0" and a newline, the most basic if HTTP Headers, the response it would get would be:
| Code Block |
|---|
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Tue, 01 Apr 2014 05:19:19 GMT Server: Apache/2.2.15 (CentOS) Last-Modified: Thu, 21 Mar 2013 05:14:21 GMT ETag: "a233b-67c-4d8686950cd27" Accept-Ranges: bytes Content-Length: 1660 Vary: Accept-Encoding Connection: close Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 |
The expect would match the data "200 OK" and declare success. More complex requests could be made here. E.g. checking a database status using HTTP.
Monitoring Services with external programs
Since version 8.4.10G nmis can also run external programs of your choice to test service statuses. To interoperate with NMIS such a program must conform to a few simple rules which are described below.
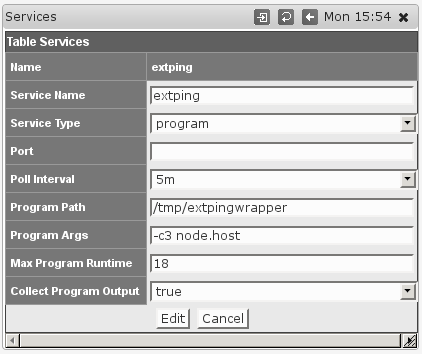
The dialog for Adding or Editing Services now shows some extra options:
Chooising the Service Type program activates the options for running external programs; they are ignored for all other Service Types.
- Program Path must point to the program in question, and must be an absolute path (i.e. starting with
/). This setting is clearly mandatory, and the program in question must be directly executable by thenmisuser. - Program Args defines arguments that are to be given to this program when run. This is an optional setting.
Any tokens of the formnode.something will be replaced by the corresponding property of this node; most likely you will want to usenode.hostfor the node's dns name or network address,node.namefor the logical node name, maybe evennode.sysContact. To determine the available properties check the 'system' section of/usr/local/nmis8/var/yournode-node.nmis. - Max Program Runtime sets the upper limit (in seconds) for how long NMIS will wait for this program to complete.
If the program has not finished by that time then it's terminated forcibly and the service is marked 'down'. This setting is optional, but highly recommended - if you don't set a limit then a single uncooperative external program could delay all NMIS collect or update operations indefinitely! - Collect Program Output defines whether extra output by the program is to be collected and stored, or ignored.
The external program must follow these interfacing rules to work with NMIS:
- Your external program must report the service status by returning an exit code between 0 and 100 inclusive.
0 means the services is down, any other value NMIS interprets as service is up. The service graphs do show the precise value, however. - Your external program can't read from stdin, and needs to finish its work and terminate as quickly as feasible; NMIS cannot proceed with further operations until the external program terminates.
- Your external program may report back to NMIS by printing
key=valuepairs on stdout, one pair per line.
If the Collect Program Output option is enabled, then NMIS will collect these values and store them in the RRD database and the node file.
The keyresponsetimeis special: any numeric value given for it will be used directly in the service and service response time graphs.