Introduction
NMIS8 is a powerful network management system which performs Windows and Unix server monitoring out of the box. NMIS8 supports Windows servers as well as the popular NET-SNMP SNMP daemon, which is widely used on Linux and other Unix systems. The core of NMIS server management is the Host Resources MIB, which is standardised in RFC2790, both the NET-SNMP, Windows SNMP and VMware ESXi daemons implement the Host Resources MIB.
NMIS8 has capabilities for performance and fault management of servers as well as service (application) monitoring running on servers.
NMIS8 collects and stores the following performance data from servers:
- Processor load
- Physical memory usage (not currently available from VMware ESXi)
- Virtual memory usage (not currently available from VMware ESXi)
- Disk usage (capacity and used)
- Network interface usage
Service Monitoring
- Checks Host Resources MIB for service status
- Performs poll of TCP/UDP port
- Runs a script which returns status (can perform full transaction over system and is highly extensible)
You can download NMIS from the Opmantek webpage.
Windows Server Support
Depends on Windows SNMP Service (often referred to as agentless server monitoring). NMIS will collect the following information from Windows Servers in addition to the already described information.
- IP Utilisation
- Server Memory Pages per Sec
- CPU Interrupts
- Memory Stats (commited and available bytes)
- Number of Users
All of these information requires no Agent to be installed onto the Windows server other than the freely available Windows SNMP Service (part of the Windows installation and setup).
Unix Server Support
Depends on NET-SNMP daemon being installed and configured, usually installed by default on most Unix platforms. Instructions for installing the NET-SNMP daemon are included in the NMIS 8 Installation Guide.
Configuring NMIS to Monitor Services
An updated services file "Services.nmis" was distributed with later NMIS8 versions, and is attached to this page Services.nmis, this is compatible with earlier versions of NMIS8. This file includes definitions for using the script method to poll HTTP, as well as monitoring for a MySQL daemon, and various ports using NMAP connections. Once Services.nmis is copied to /usr/local/nmis8/conf, you should verify that you have the scripts folder in nmis8, this is included in the install directory "cp -r /usr/local/nmis8/install/scripts /usr/local/nmis8/conf" will make that happen.
When a service "outage" is detected you will receive NMIS events and notifications if NMIS has been configured to do so.
Step 1
From the NMIS Menu, navigate to "System -> System Configuration -> Nodes (devices)"
Step 2
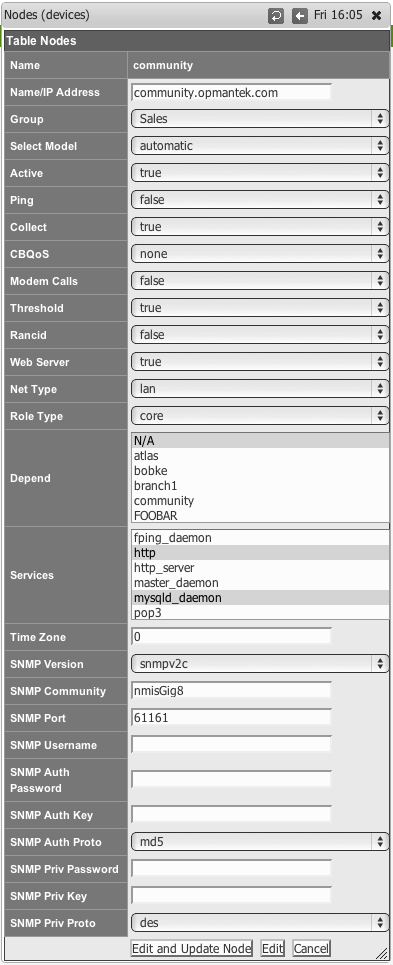
From the list of nodes, select "edit" from the server you want to monitor services on.
Step 3
From the services box, select the services you want to monitor, you can select several services.
Step 4
When you are done, select "Edit and Update Node", after the next poll cycle runs, within about 5 minutes you will see that the services are now being monitored
Step 5
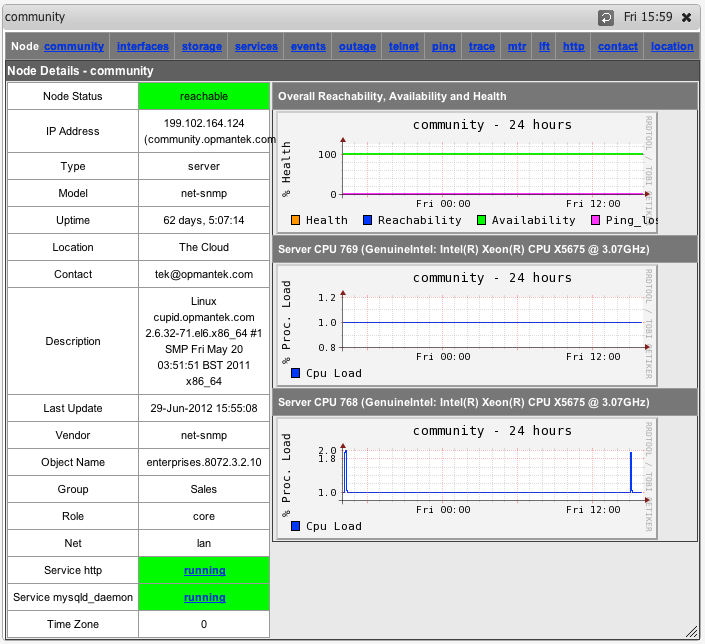
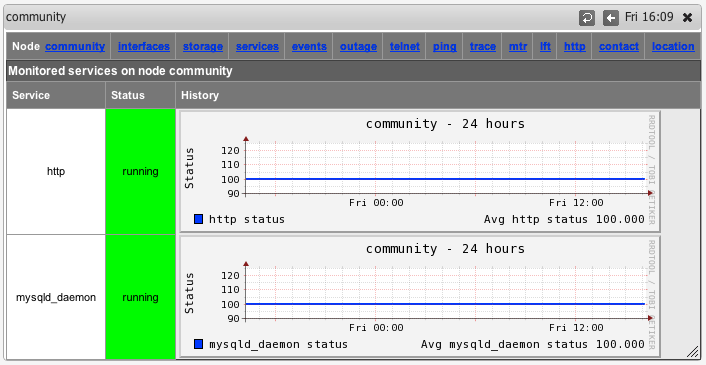
You can also now select "Services" from the node menu bar and see a graph of all the monitored services.
Defining new Services to Monitor
Step 1
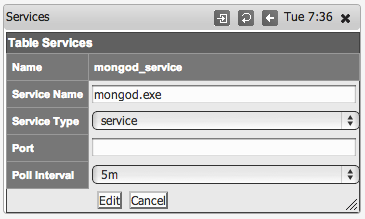
Determine the name of the service you want to monitor, for example to Monitor MongoDB on Windows, the process name is mongod.exe.
Step 2
From the NMIS Menu, navigate to "System -> System Configuration -> Services"
Step 3
Then select add or edit to add a new service or edit an existing service monitoring definition.
Step 4
Give the service a name, for Windows we call them service and for Unix we call them daemons. Select the Service Type of service which is an SNMP monitored service.
Step 5
Click "Add" or "Edit" to save the new service and then you can assign this to a device as described above in "Configuring NMIS Services to Monitor".